Project Euler 144: Laser Beams and Elliptical Billiards

Peter Prevos |
1217 words | 6 minutes
Share this content
Playing pool at a square table can be hard enough for most people. But what about testing your skills on an oval table? Project Euler 144 investigates multiple reflections of a laser beam. This problem is mathematically equivalent to bouncing billiard balls in an elliptical pool table, demonstrated by Ales Bellow in the video below. This article provides a solution to the Euler problem and simulates playing pool in an elliptical table.
Project Euler 144 Definition
In laser physics, a “white cell” is a mirror system that acts as a delay line for the laser beam. The beam enters the cell, bounces around on the mirrors, and eventually works its way back out.
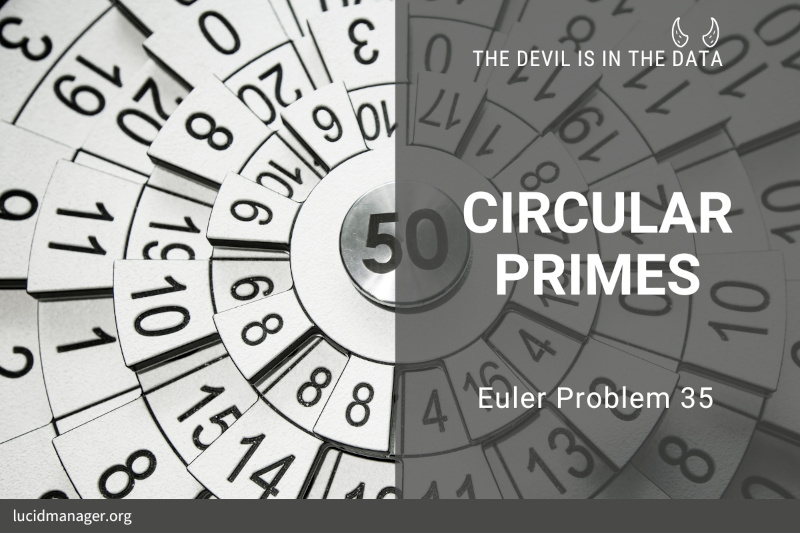
The specific white cell we will be considering is an ellipse with the equation $4x^2 + y^2= 100$. The section corresponding to $-0.01 \leq \times \leq +0.01$ at the top is missing, allowing the light to enter and exit through the hole.
The light beam in this problem starts at the point (0.0, 10.1) just outside the white cell, and the beam first impacts the mirror at (1.4, -9.6). Each time the laser beam hits the surface of the ellipse, it follows the usual law of reflection “angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.”
Both the incident and reflected beams make the same angle with the normal line at the point of incidence. In the figure on the left, the red line shows the first two points of contact between the laser beam and the wall of the white cell; the blue line indicates the line tangent to the ellipse at the point of incidence of the first bounce.
The slope $m$ of the tangent line at any point $(x,y)$ of the given ellipse is $m = -4x/y$. The normal line is perpendicular to this tangent line at the point of incidence.
How many times does the beam hit the internal surface of the white cell before exiting?
Proposed Solution
The first step was to rewrite the equation to use functions to generalise the problem. The general Cartesian equation for an ellipse is:
$$\frac{x^2}{a^2} + \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1, a < b$$
The length of the axes for this problem is $a =5$ and $b = 10$. While the Project Euler description gives the formula for the tangent slope to the ellipse, I have generalised the code to reuse it for the elliptical billiards table. The slope of the tangent to an ellipse at point $(x,y)$ is:
$$m=-\frac{b^2x}{a^2y}$$
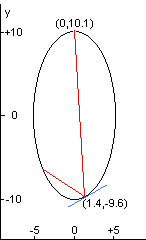
This first code snippet defines functions to draw an ellipse and calculate the bouncing angle. The last part of the code bounces the laser inside the cell until it exits through the top.
The formula to find the intersection between a line and an ellipse has two possible solutions, one of which is the same as the original point.
plot_ellipse <- function(a, b, colour = NA, line = "black") {
plot.new()
plot.window(xlim = c(-a, a), ylim = c(-b, b), asp = 1)
par(mar = rep(0,4))
x <- seq(-a, a, length = 200)
y <- sqrt(b^2 - (b^2 / a^2) * x^2)
lines(x, y, col = line)
lines(x, -y, col = line)
polygon(x, y, col = colour, border = NA)
polygon(x, -y, col = colour, border = NA)
}
bounce <- function(coords) {
x <- coords$x
y <- coords$y
## Tangent to ellipse
t <- -(b^2 / a^2) * (x[2] / y[2])
## Deflection on sloping mirror y = mx + c
dydx <- diff(y) / diff(x)
m <- tan(pi - atan(dydx) + 2 * atan(t))
c <- y[2] - m * x[2]
## Determine intersection point
## Source: http://www.ambrsoft.com/TrigoCalc/Circles2/Ellipse/EllipseLine.htm
x[1] <- x[2]
y[1] <- y[2]
x2 <- (-a^2 * m * c + c(-1, 1) * (a * b * sqrt(a^2 * m^2 + b^2 - c^2))) /
(a^2 * m^2 + b^2)
x[2] <- ifelse(round(x[1] / x2[1], 6) == 1, x2[2], x2[1])
y[2] <- m * x[2] + c
return(data.frame(x, y))
}
# Initial conditions
a <- 5
b <- 10
x1 <- 0
y1 <- 10.1
x2 <- 1.4
y2 <- -9.6
answer <- 0
plot_ellipse(a, b)
points(c(0,0), c(-c, c), pch = 19)
## Bounce laser breams
laser <- data.frame(x = c(x1, x2), y = c(y1, y2))
while((laser$x[2] < -0.01 | laser$x[2] > 0.01) | laser$y[2] < 0) { ## Escape?
lines(laser$x, laser$y, col = "red", lwd = .5)
laser <- bounce(laser)
answer <- answer + 1
}
print(answer)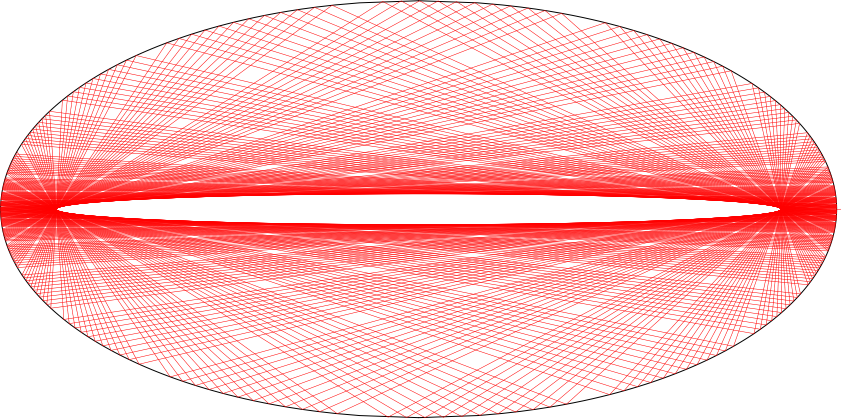
Elliptical Pool Table
We can use the solution to Euler problem 144 to play billiards on an elliptical billiards table. To close the article, we return to the elliptical pool table demonstrated by Alex Bellos. This code draws the pool table to the dimensions mentioned in the video. We know that the table has an eccentricity of $e = 0.43$ and a long axis of $a = 130$ cm. The code defines the short axis ($b$) and the distance of the focal points from the centre.
The code selects a random starting point and angle of the shot. The code first determines whether the line passes through the pocket. If this is not the case, the algorithm then finds the place where the ball hits and keeps bouncing it until it falls into the pocket, or the ball bounces 100 times.
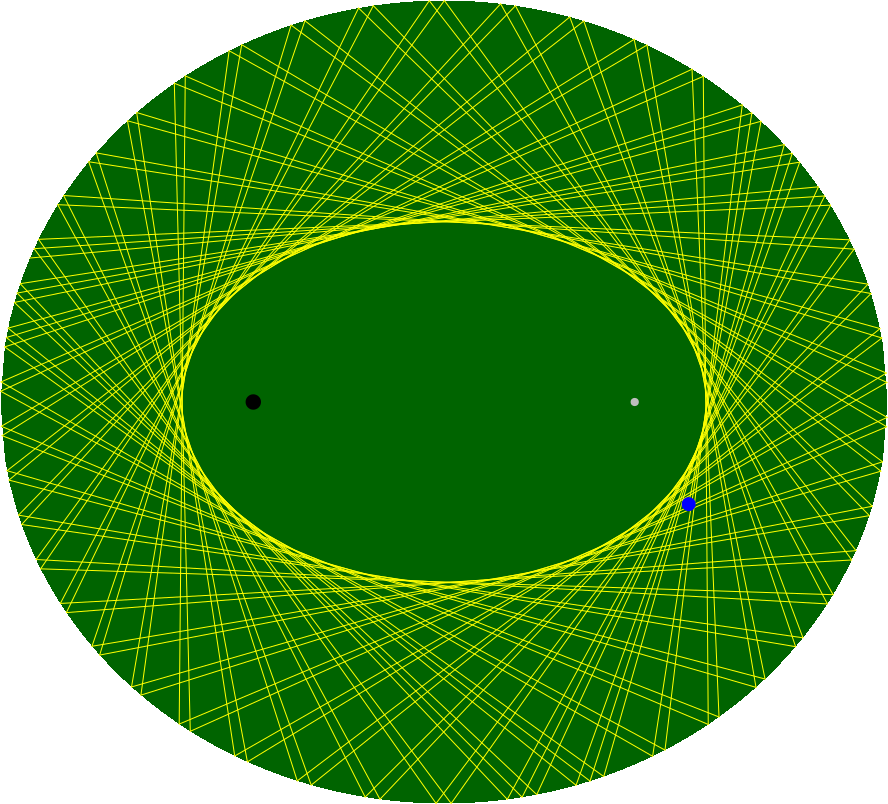
Elliptical billiard tables have four possible outcomes. Any ball the pass through a focal point will fall into the pocket, ending the simulation. Any ball that passes outside the focal points will bounce around, and the combined trajectories form an ellipse. When the ball moves between the foci, the result is a hyperbola. Lastly, some unique circumstances result in a regular polygon.
If simulations are not enough for you, then head over to the Instructables website to find out how you can construct an elliptical billiards table. There is even a patent for an elliptical pocket billiard table, with the pockets at the edge.
e <- 0.43
a <- 130
b <- a * sqrt((1 + e) * (1 - e)) # a > b
f <- sqrt(a^2 - b^2)
plot_ellipse(a, b, "darkgreen", NA)
points(-f, 0, pch = 19, cex = 2)
points(f, 0, pch = 19, col = "grey")
## Simulate random shot
angle <- runif(1, 0, 2 * pi)
x1 <- runif(1, -a, a)
ymax <- sqrt(b^2 - (b^2 / a^2) * x1^2)
y1 <- runif(1, -ymax, ymax)
## First shot
m <- tan(angle)
c <- y1 - m * x1
x2 <- (-a^2 * m * c + c(-1, 1) * (a * b * sqrt(a^2 * m^2 + b^2 - c^2))) / (a^2 * m^2 + b^2)
y2 <- m * x2 + c
x2 <- x2[which(((x2 - x1) < 0) == (cos(angle) < 0))]
y2 <- y2[which(((y2 - y1) < 0) == (sin(angle) < 0))]
shot <- (data.frame(x = c(x1, x2), y = c(y1, y2)))
## Bounce ball
for (i in 1:100){
dydx <- diff(shot$y) / diff(shot$x)
if (all.equal(dydx, (shot$y[1] - 0) / (shot$x[1] - -f)) == TRUE) {
shot[2, ] <- c(-f, 0)
}
lines(shot$x, shot$y, col = "yellow", lwd = 1)
if (shot[2,2] == 0) break
shot <- bounce(shot)
}
points(x1, y1, pch = 19, col = "blue", cex = 1.8)Share this content